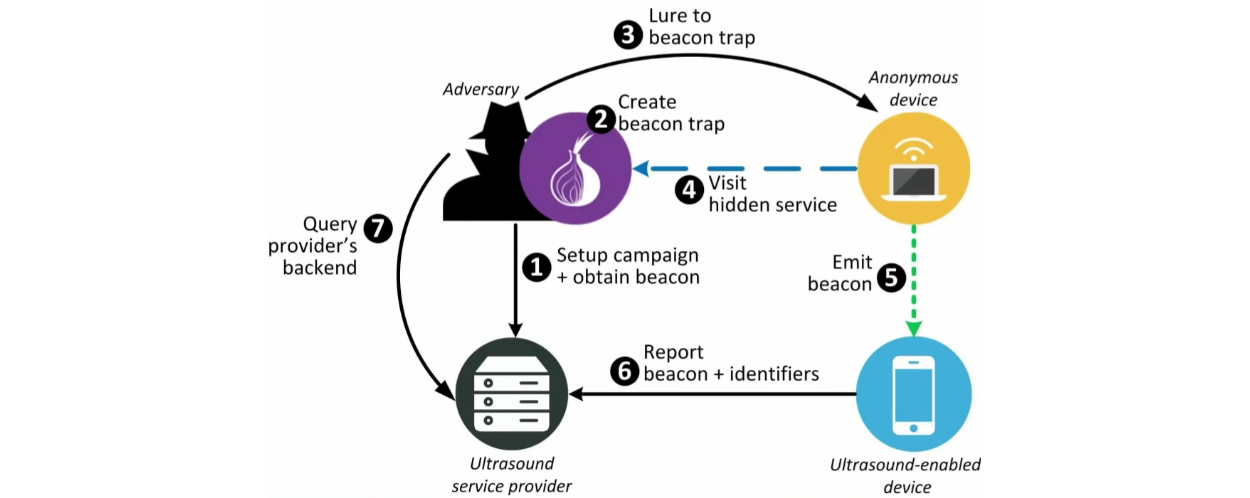
Ultrasounds emitted by ads or JavaScript code hidden on a page accessed through the Tor Browser can deanonymize Tor users by making nearby phones or computers send identity beacons back to advertisers, data which contains sensitive information that state-sponsored actors can easily obtain via a subpoena.
This attack model was brought to light towards the end of 2016 by a team of six researchers, who presented their findings at the Black Hat Europe 2016 security conference in November and the 33rd Chaos Communication Congress held last week.
Attack relies on ultrasound cross-device tracking (uXDT)
Their research focuses on the science of ultrasound cross-device tracking (uXDT), a new technology that started being deployed in modern-day advertising platforms around 2014.
uXDT relies on advertisers hiding ultrasounds in their ads. When the ad plays on a TV or radio, or some ad code runs on a mobile or computer, it emits ultrasounds that get picked up by the microphone of nearby laptops, desktops, tablets or smartphones.
No comments:
Post a Comment